THE FIRST PART CAN BE FOUND HERE: Main Battle Tank Development Concept Of German Army (Part 1)

Leopard II battle tank is pictured in action at the Oberlausitz training area in Weisskeissel. Source: Reuters
Written by V. Boryushin, V. Sokolenko; Originally appeared at Foreign Military Review #3 2019, translated by AlexD exclusively for SouthFront
In the first part of the article the main directions of development of Germany’s CVA in the near future, the course of measures on modernisation of the existing park of tanks of the country, the concept of the MBT development and information on the creation of the Leopard tank of the prospective 2A8 (2A7V) series were covered.
The main battle tank is the Leopard-3. The creation of a new generation of MBT of Germany’s military-industrial leadership is associated with the development of the Leopard-3 tank, or Leo 3, as it was originally called in the Bundeswehr. Currently, foreign experts also use the term “Main Ground Combat System”.
In NATO countries, the ground combat system (GCS) is understood as a set of samples (complexes) of weapons that are functionally related to each other and are jointly used to solve certain combat tasks.
The GCS usually consists of 10 to 18 types of armoured vehicles operated by a person. These include tank, AIFVs, APCs; command vehicles of the company-battalion-brigade link; combat reconnaissance vehicle; self-propelled gun howitzer; self-propelled mortar; repair and evacuation vehicle; medical vehicle and others; from four to seven types of unmanned vehicles, remotely controlled by humans as well as unmanned aerial vehicles of different classes and purposes, armed with ground-based unmanned vehicles, multi-purpose general-purpose vehicles for technical and logistics support.
The German Ministry of Defence first announced plans to create a new-generation main battle tank as part of the GCS programme on May 22, 2015. For its development, the leading German manufacturer of armoured vehicles, KMW, intends to join forces with the famous French tank-building company Nexter Systems.
A new German-French company with more than 6,000 employees and a total financial turnover of about 2 billion euros ($2.2 billion for 2015) may become the main contractor able to win a contract for the development and production of the MBT for the Bundeswehr, France and other countries of the Alliance.
To date, the technical appearance and design features of the promising tank are in the design stage. Speaking in the Bundestag, German Deputy Defence Minister Markus Grübel said that “the concept of the new tank and the main technologies for its creation are planned to be developed in the period from 2015 to 2018. The issues of joint R&D with the German industry have already been agreed upon.”
The commander of the German Armed Forces, Lieutenant General Joerg Vollmer, noted in early 2017 that “all Leopard-2 tanks currently in tank and motorised infantry brigades will be completely replaced with the main GCS in the period from 2030 to 2040”. This system will be able to “conduct dueling combat and deliver fire strikes in close combat within a line of sight”.
From foreign information, it follows that the priorities in the development of the German-French machine will be given to ensuring the maximum survival of the crew in combat, giving the MBT maximum combat effectiveness in various types of combat, and achieving a low cost of production.
When developing the new tank, innovative technologies will be used to ensure the ability to conduct network-centric combat operations in the information networks of the tactical level of the types and branches of the armed forces of Germany and other NATO countries.
The firepower and mobility of the MBT is planned to increase considerably compared to existing models.
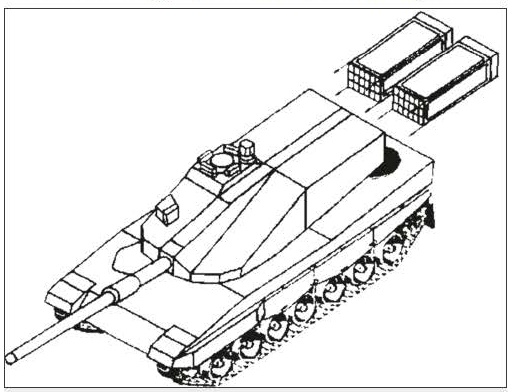
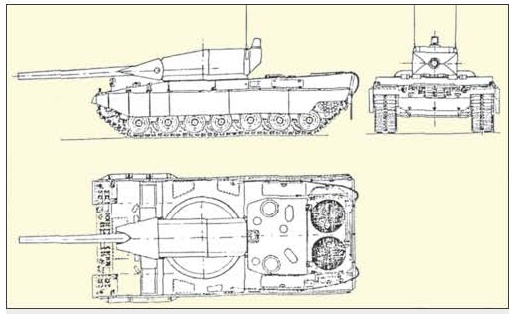
Conceptual views on the design and layout schemes of the Leopard-3 tank. The technical projects of the new generation tanks created earlier in Germany make it possible to form the following idea about the technical appearance and design layout of the new combat vehicle.
Project of the 1981-1996 years. This German-French tank had the following structural and technical features: a crew of three people (two of them, the commander and the gunner, in a flat low-profile turret); a 120-mm and in the future, 140-mm smoothbore gun; automatic gun loading in the niche of the turret; an automated system for loading and unloading ammunition on the battlefield from a transport-loading vehicle; the chassis of the Leopard-2 tank.
However, consensus could not be reached between the participating countries, and in November 1982 France withdrew from the R&D. After that, the German part of the project was named Leopard-3. Research was carried out in the following areas: development of a new turret on the chassis of the Leopard-2 tank, a new low-profile non-armoured turret and new chassis. However, this programme was terminated due to the lack of relevance of the work carried out at that time, and the emergence of priority R&D aimed at increasing the caliber of tank guns.
Project of the 1985-1996 years. This is one of the first MBT projects of a new generation with two crew members.
The western military media previously reported that a demonstration model had already been developed, testing of which showed that “with the technical level of automation of work processes, which is typical for that time, a crew of two people can perform all the tasks assigned to it as successfully as a crew of three or four people”.
With this in mind, KMW began to develop a concept for the overall protection of an experimental tank with a 140-mm gun (with a non-armoured, remote-controlled turret) and two crew members located in the front of the hull. The experimental prototype was named EGS.
The layout of its hull was similar to the tank test-bench of the TTV, created in the US by GDLS in the early 1980s on the order of the command of the United States Army Tank-Automotive and Armaments Command (TACOM). However, the American version of the experimental tank had a crew of three and demonstrated the advantages of placing all crew members in the hull, although its critical frontal zone (which protects the crew) was only 2.77 m2 compared to 3.59 m2 for the M1 Abrams tank, on the chassis of which the TTV test-bench was created.
The critical frontal zone of the EGS tank was even smaller, which made it possible to cover it with armour of greater thickness without increasing the mass of the vehicle.
This layout principle clearly proved the advantages of such a design and layout solution, as it allowed to have a frontal armour equivalent to rolled homogeneous armour with a thickness of more than 1,000 mm. In addition, placing the crew inside the tank body outside the turret increased its survival rate. Despite the significant improvement in the protection of the tank with a two-man crew, many military experts rated this variant of the layout negatively due to the inability of two people to effectively control the tank in combat for a long time (more than 4 hours).
In addition, R&D results have shown that it is necessary to recognise the limited endurance of a two-person crew when driving a tank in combat for a long time.
It was suggested that two crews should be prepared for each tank, which could replace each other in the course of long-term combat operations. However, the military leadership in Germany and officers with combat experience expressed their doubts about the possibility of successfully replacing the crews in a combat situation.
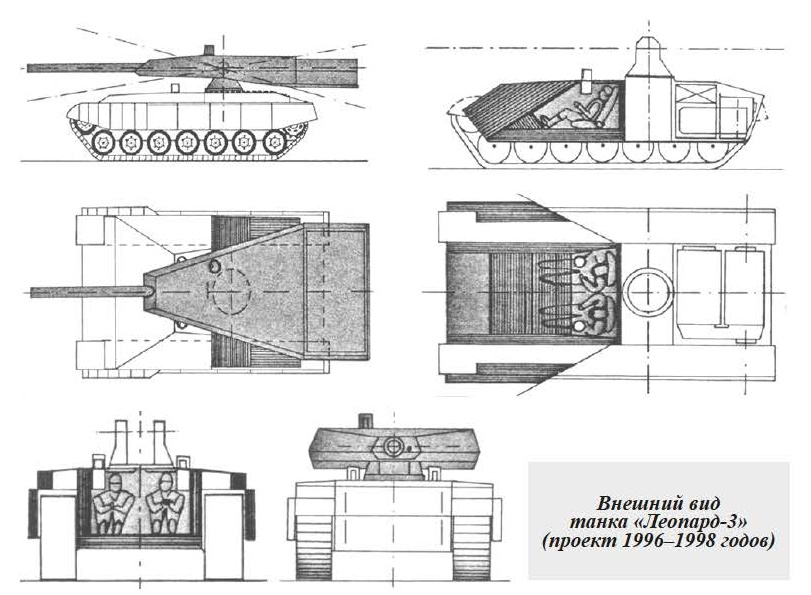
Project of the 1996-1998 years. Here, the promising machine was considered as a tank of the XXI century, which was planned to introduce the following technical innovations: a smooth-bore 140-mm gun that fires separate loading ammunition; an automatic loader in the turret recess; a compact fighting compartment with two crew members; an electric transmission; as well as carry out a set of measures to strengthen the overall protection, especially in the frontal plane; measures to reduce infrared and radar visibility; active protection system; advanced fire control system of the new generation; digital architecture of the on-board information system of the open type.
The new layout of the tank with a crew of two people focused on the use of new technologies, allowed to protect the frontal projection of the vehicle with armour with an equivalent thickness of rolled homogeneous armour equal to 2000 mm. The project remained unrealized, because at first there were problems with coordinating tactical and technical requirements with the industry, and later, due to the changed military and political situation in the world and insufficient funding.
Conducting a full-scale R&D in the current environment was considered irrelevant and untimely.
Project of the 1996-2004 years. It was developed under a programme called NGP (New Armoured Platforms). This was the first German programme, according to which it was planned to create machines for the benefit of the land forces, a ground combat system. When developing the project, for the first time in foreign practice, it was planned to implement the principle of using a common unified 50-ton tracked chassis as a single base for three types of vehicles (tank, AIFV, APC). It was supposed to create three types of unified platforms: type A – the main battle tank, initially with a 120-mm, and later with a 140-mm gun; type B – a highly protected AIFV; type C – a heavy tracked general purpose armoured personnel carrier for transporting infantry.
The arrival of the type A platforms in the army was to begin after 2012, taking into account that the service life of the Leopard-2A5 tank expired in 2015, and serial production of the types B and C platforms was planned to begin in 2009, in order to timely replace the fleet of tracked Marder ARV and wheeled (6 x 6) Fuks APCs.
The main goal of the NGP programme was to reduce the number of tank crew members from four to three or two.
In studies conducted in Germany in collaboration with KMW, the effectiveness of the combat work of the tank crew of two people was evaluated, provided that the crew was replaced every 12 hours, so that the tank could be operated without interruptions for several days. The NGP programme was closed in 2004 due to the high complexity and cost of work, and mainly due to the change of priorities of the German ground forces command in favour of the development of the Puma BMP (R&D began in 2002) and the programme for the creation of the boxer armoured personnel carrier (in 1999). The NGP programme ended with the creation of a demonstration chassis layout for a promising tank.
Project of the 2001-2005 years. It was developed by the German firm KMW proactively based on the conceptual provisions of the project as outlined in the report “Alternative Weapons for Combat Platforms of the Future”, made by the KMW representative. In this document, when justifying the main directions of weapons development, and in particular the new generation of MBTs, it was argued that the disadvantages of modern concepts that determine the firepower of combat vehicles are the following: the tank’s rocket and gun armament cannot be used simultaneously for different ground and air targets; it is impossible to control these weapons by “direct calls” from the infantry and other attached units, or it takes too much time, which increases the time spent on hitting the target, and does not provide the required flexibility in using the tank’s weapons system.
The key element of the new weapons system should be, according to German experts, the use of vertically launched missiles with the control of the “shot-forgot” type. Such missiles can be used to destroy unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), helicopter gunships, or used against a wide range of ground targets (tank units on the march and in areas where they are concentrated, against command posts and other important near facilities, and others).
It was planned to install eight to ten guided missiles in the launch containers in a vertical position, which could be launched in any direction, at any time, regardless of whether the gun is fired or not.
In accordance with the project, the new MBT should have a crew of three: two operators sitting side by side in the front of the hull (the operator, gunner and the operator-commander of the machine), and a driver. It was planned that the tank would be armed with a 140-mm gun (with an ammunition supply of 30-32 rounds) and vertically launched guided missiles located in the niche of the turret. The concept of the tank’s weaponry was first developed in the framework of the NGP.
Conceptual views of the main directions of development of combat properties of the Leopard-3 tank.
Fire power. German experts believe that the creation of a new generation of MBTs will be closely connected with the increase in the caliber of the tank gun, so the development of tank weapons and ammunition should become a priority in the near future. At the same time, it is emphasized that the upper limit of the tank gun caliber has not yet been reached and can be increased to 140- 155-mm due to design and layout solutions, although expensive and complicated.
As noted in the materials published in the western military media, the increase in caliber is necessary in order to guarantee that heavy armoured combat vehicles can be hit from a long distance. At the same time, foreign sources indicate that the effectiveness of modern tank ammunition has already reached the maximum value, when 120-mm armour-piercing sub-caliber projectile (APS) and cumulative projectiles (CP) no longer provide the armour-piercing characteristics that promising tank guns above the specified caliber can provide.
At the same time, the experience of installing a 140-mm gun in a tank has shown that there are many complex technical problems along this path that cannot be solved quickly by modern scientific and technical methods. The main one is the development of automatic loading guns with unitary 140-mm ammunition.
The transition to separate charging for many reasons is recognised by German experts as impractical for the following reasons: it is impossible to maintain the tank’s internal dimensions of ammunition within 40-45 units (while reducing the 140-mm ammunition to 28-30 pieces is considered unacceptable from a tactical point of view), as well as due to the need to install a partially or fully automated ammunition loading/unloading system in the tank. The development of such a system requires the creation of special transport loading tracked vehicles, making significant changes to the existing design of the body and especially the machine’s turret. In general, the solution to these problems, according to foreign experts, is associated with time-consuming and expensive measures, which in terms of their costs and complexity of R&D is comparable to the creation of a new tank.
Under these conditions, military experts of the leading NATO countries recognise that the current military and political situation in the world and the limited military budgets of Alliance members for the development and purchase of new tanks will not allow even in the medium term (within 10-15 years) to replace the 120-mm guns with 140-mm ones.
Work priority areas on the 140-mm gun remain: the creation of a loading machine, the development of new ammunition, the creation of a system for automated loading of ammunition into a tank from a transport-loading machine. The final decision to start mass production is delayed today due to insufficient funds allocated for the development, refinement and production of the required number of such ammunition.
Another limiting factor in the development of the gun is the high efficiency of innovative technologies introduced to further improve the characteristics of the 120-mm gun, ammunition and the tank’s weapons control system (WCS).
Currently, German experts believe that the progress made in the development of modern technologies in the field of tank guns, ammunition and fire control systems makes it possible to achieve a level of performance of the 105-mm tank guns close to the characteristics of the 120-mm guns of the first generation, and the new generation of 120-mm tank guns is comparable to the characteristics of 130-mm guns.
The existing successes in the development and implementation of innovative technologies for improving the 120-mm gun, its ammunition, and the WCS forced German specialists to reconsider their views on the further development of tank weapons, which was due to technical difficulties in solving scientific problems associated with the installation of large-caliber guns in the MBT.
For these reasons, Rheinmetall specialists became confident in the early 2010s that the characteristics of a 140-mm gun could be achieved by creating a 130-mm gun, provided that its technical level, ammunition, and WCS were brought to a certain level of perfection.
As a result, in the long term (over 15-30 years), it will be possible to limit the increase in the caliber of the tank gun to 130-mm. In this case, a number of scientific and technical problems associated with increasing the caliber of tank guns to 140-mm can be solved at a lower cost, cheaper and technically in a less complex ways.
The 130-mm smoothbore tank gun created by Reinmetall was shown to the general public for the first time in June 2016 at the Eurosatory arms exhibition in Paris. The gun differed from the 120-mm serial prototype in having a shorter barrel length (51 calibers instead of 55), a vertical-falling wedge bolt, an increased chamber volume and a chrome-plated bore surface.
Its mass, including anti-rollback devices, was about 3000 kg, the barrel weight was 1400, while the muzzle brake was not provided and was absent.
The prototype shown at the exhibition had an ejector, a heat-insulating gun barrel casing and a system for automatic alignment of the sight during thermal bending of the barrel. As reported in the advertising and technical brochures of the company, the gun is intended for installation on a new-generation Leopard-3 tank, as well as the MBT Leopard-2 series during their modernisation.
It was stated that at the current development stage of the 130-mm tank gun, two types of unitary ammunition should be considered as priority areas of work: armour-piercing sub-caliber feathered projectile with detachable leading parts, which will have a partially combustible sleeve, an increased volume and improved physical and chemical composition of the propellant, an elongated, compared to the 120-mm APS, tungsten core; a high-explosive air-detonating projectile that is being developed on the basis of the 120-mm DM11 munition currently in production for the domestic and foreign markets and used for firing 120-mm L44 and L55 tank gun.
During the development of the 130-mm ammunition, one of the most important areas was to reduce the explosion and fire safety of ammunition when it is used in a tank, including in the case of armour pentation, which is the main requirement of most modern customers of this ammunition.
Western military experts believe that the 130-, 140-mm smoothbore gun will be used as the main armament of the next-generation tank, and it will be possible to fire guided ammunition. Observation of the environment from the tank will be carried out using a system of electronic sensors (implementation of the principle of “observation through the armour”). The following types of unitary ammunition are under development: an armour-piercing feathered projectile with detachable launch charges and a high-explosive air-detonating projectile.
The plan is to fire the cannon from the driver’s seat.
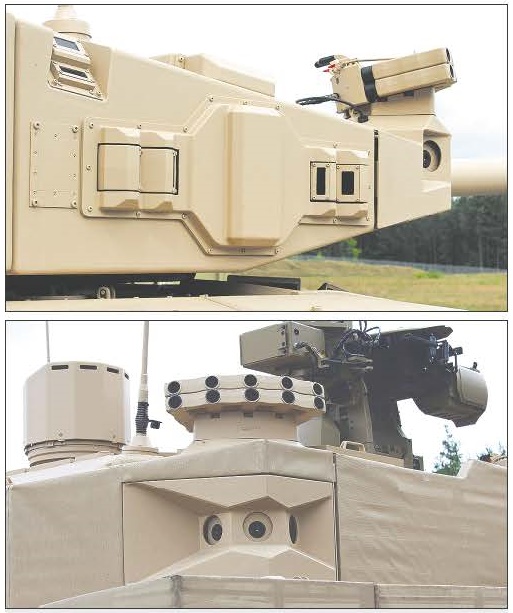

For the main battle tank of the new generation, military customers make demands to ensure full-fledged circular protection of the vehicle from most current and future threats.
Protection. Military customers make demands to ensure all-round protection of the tank against most current and future threats, especially when attacking the upper hemisphere. For this purpose, it is planned to use modular armour protection developed on the basis of nanotechnologies (nanosteel and nanocomposite materials), so that the increase in the combat weight of the tank is relatively small. Among other requirements, the following are highlighted: ease of installing additional armour protection on the outside of the tank, as well as minor changes to the design of the vehicle’s hull and turret when installing armour modules.
The basic version of the modular armour system needs to protect the crew from high caliber shotgun, precision guided munitions and guided and unguided antitank weapons, the roof of the hull and turret from cluster munitions, side protection of the hull and turret from mines and IEDs, including fragments of 155-mm caliber artillery shells and the protection of the lower part of the hull from mines and IEDs.
Other requirements are also known: the firing pad must be located outside the combat compartment zone, the system for setting a circular smoke (aerosol) curtain must be triggered after detecting a threat in the visible, thermal, television and radar waves ranges for a period not exceeding 0.5 seconds. It must also be operable in motion.
Mobility. A number of measures aimed at improving the mobility in various tank’s combat application are planned, including controlling the movement of the vehicle from the commander’s and gunner’s workstations, short-term increase in power on the drive wheels, insuring for a short time silent and emergency movement when the main engine is idle. These modes of operation of the power unit is planned to be realised by connecting the main motor of the auxiliary power plant of increased power, as well as electrical and mechanical (inertial type) energy storage devices.
Command controllability. It is planned to increase by about 2-3 times the amount of electrical power generated on board the tank to supply the increased number of on-board electronic systems by using more powerful auxiliary power units. The levels of automation and “intellectualisation” of combat and work processes that take place during firing and in motion will be significantly increased to ensure survivability and command control.
All tanks will be equipped with standard remote-control equipment, which will, if necessary, enable the crew-free operation of the combat vehicle.
Thus, the further development of the main battle tank in Germany is carried out at the present stage in two separate directions: the modernisation of the Loepard-2 tank series to the A8 modification and the creation of a new generation of MBT Leopard-3. According to the first direction, using modern technologies, the design of the Leopard-2 tank is planned to be brought to the maximum level of perfection, including by creating and installing a next-generation tank gun on it.





Not bad.
Its basically a scaled up Tiger.
Its in the top 5.
and just as ineffective as the Turkeys found out in Syria.
The dumbass Krauts should have steered clear of USSR because as soon as they faced the Russian legendary T-34, they were cooked. Generally considered as the Red Army tank that won WW2.
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/8dd870ce2f2dfb41a9cc3ffa8bac5b9d80e9b9b46cde8341a2f5c0227fef81f9.png
Don’t under estimate German engineering. Germans contributed a lot to science and military R&D. Also it was the American military aid (nearly one trillion dollars in today’s currency) to Russia which saved Russia from annihilation in WW2. Even the famous Katyusha rockets were mounted on US made trucks.
The truth is, that the T-34 in the beginning was a total fiasco. Zhukov had removed in summer 1942 all of them. Got new engine, better canons, radios. After this rebuilding began to be good tanks.
It was the first mass produced Russian tank and upgrades made it the best. They are still being used in Yemen. Russian tech is simple, reliable and lasts for ever. Look at Lada and Moskvich cars.
lada and moskvich úlus zaporozhets, volga are shits
Volga decent, especially trucks–now lada decent—moskvitch is designed for midgets
This is the gear that I’m planning on bringing for my upcoming caldera op.
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/657ecf9bcc15797a7f61cf04c6d7db1e0640b277f41bc3f8b0513a81975937b2.jpg
The nightime bigfoot caldera encounter 3 years ago where I heard what sounded like a ship field drive, may have been with a family unit from the sounds of it. The alpha males in this area can grow to 8 or 9 feet tall and weigh 750 or more pounds according to reports. Depending on how ripped or heavy they are.
The para 550 cord is rated for 550 pounds of line strength. If I need more than 300 feet for the steep sections where it’s 3 and 4 contact point climbing, it’s light enough that I can bring more. I’m planning to put hand hold loops in about every 3 feet.
There are two ways into the caldera that rises as part of a river gorge ridgeline about 3,800 feet up from the river to the rim. There’s an 800 foot deep about a 60 degree at the rim V shaped break in the caldera wall where a ravine runs down the head wall 3,000 feet to the river. That the disappearing lake drains out to through the gravel floor to springs at the top of the ravine.
When the lake is empty the gravel bottom will support a heavy ship without risk of the landing gear sinking into the surface.
There’s an abandoned logging road spur that ends 2,300 feet up the head wall facing the river at the ravine. The last two times that I was up there, the night of the encounter, and a follow up day time investigation a few days later. I parked my Bronco ll at the ravine and climbed and scaled the last 700 vertical feet to the bottom of the break in the caldera wall.
The second time that I made it up into the caldera during the day. I continued to climb up out of the caldera to the rim on the back side of it from the river. Where I found a trail that winds down the outside of the caldera cone down to the logging road about 3 miles away. It’s about a 1,000 foot vertical drop.
I used Google Maps satellite and topography views to assess the area. It looks like there may be an easier way down into the Caldera from the rim trail high point. The head wall approach from the logging road spur is difficult, time consuming and dangerous. Descending and ascending from the rim may be easier and safer. But I’m bringing 300 feet of line just in case.
Once I find the best way in and out of the disappearing lake basin at the bottom of the caldera. I’ll then run an overnight op and see if anything non conventional happens. The second time that I made it into the caldera on the follow up op. It was dark by the time that I got back to the truck. There was an unidentified light about 1 mile down the ridgeline where it would have been difficult for a human to access in a no trail area.
It may have been a probe. If it happens again and approaches me I’ll video it. I’m researching video hosting options to be able to include them in posts here.
.40 S&W hard cast lead 200 grain dangerous game rounds with 2 to 3 feet of pentration capability.
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/f8dc96e35a05a14f0186c664ae087b782a28bed456bb9e25519431a8ab5fbee5.jpg
9mm +P 147GR thick FMJ-FP dangerous game rounds with 1 to 2 feet of penetration capability.
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/c1d5487dc7615018613fe365ac979914c0de40dc02f1b01189764161c4e5b2ff.jpg
The average breaking test for 550 cord was 804 pounds. As long as I’m careful to avoid sharp edges during the line placement. It should get the job done for a steep grade climbing assist if I’m careful.
https://youtu.be/5qvHu0e3D_0
Electronics gear for contact ops. Emergency location beacon with 10 second interval location tracking, SOS alarm to call center and smartphone Bluetooth two way texting capability. 4 track digital stereo sound recorder. Gopro hat with camera and light.
https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/53e9dec757d5027295dfa781c0c5d705fb62ab578d7f85e45099e82de8bf5232.jpg
I’m not trying to instigate or arrange an alien invasion. At this stage I’m simply looking for better medical care for my parents and ETs that can participate in our positive transition into becoming a positive ET race ourselves. By intermediating with our planet’s administrations and foreign ministries.
I don’t know what to think about Alex Jones’ omnicide plan that it appears that the Satanic Jewish and Zionist elite are rolling out. Or the Plejaren’s military intervention projections to mitigate it. Or what ET military landing craft into conflict zones consist of. But it is worse case contingency planning that I’ve added to my contact work.
I just bought this rifle pack for delivery by July 17, 2020. To be able to bring my 12 gauge or .30-06 with me on an overnight caldera contact op. https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/02deac6808e9e25287029f57166e86dbaaa519b9a2a08067cc22ece8cfd514d7.png
New tank development is a big ticket item. Given the EU’s self flagulation with the scamdemic, at best it will be pushed back. And as technology advances tank obsolescence as a weapons system may become a factor with other weapons systems competing for funding.
tanks seem to be limited in difficult terrain—warfare has changed in the past 75 years…today there are portable weapons that disable tanks